CNC Step Distance Calculator
For CNC machine enthusiasts, engineers, and hobbyists, precision is everything. Knowing exactly how far your CNC axis moves per step is crucial for accurate milling, engraving, or 3D printing. Our CNC Step Distance Calculator helps you determine the exact linear distance traveled by a stepper motor per step, factoring in microstepping, lead screw pitch, and gear ratios.
Whether you are building a custom CNC machine or optimizing your existing setup, this tool is designed to save time, reduce errors, and improve precision.
What Is a CNC Step Distance Calculator?
A CNC Step Distance Calculator is a specialized tool used to calculate the linear movement per step of a stepper motor. Stepper motors move in discrete steps, and combined with microstepping and lead screws, the actual distance the CNC axis travels can vary.
This calculator simplifies these calculations, providing instant results without needing manual formulas. By entering the motor’s steps per revolution, microstepping, lead screw pitch, and gear ratio, you get an accurate measurement of movement per step in millimeters.
Why Step Distance Is Important
Step distance affects every aspect of CNC machining:
- Precision Cutting and Engraving – Knowing the exact step distance ensures your cuts, holes, or engravings are positioned accurately.
- Calibration and Tuning – Helps in calibrating your machine’s motion system for consistent results.
- Reducing Errors – Prevents cumulative positioning errors over long cuts or multiple passes.
- Optimal Microstepping Usage – Guides you in selecting the appropriate microstepping for the desired resolution.
By using this calculator, CNC operators can confidently set their machine’s steps per millimeter and achieve precise, repeatable motion.
How to Use the CNC Step Distance Calculator
Using our calculator is straightforward, even for beginners:
- Enter the Stepper Motor Steps per Revolution
Most stepper motors have 200 or 400 steps per revolution. Check your motor datasheet for the exact value. - Enter the Microstepping Value
Microstepping allows the motor to move in smaller increments than a full step, increasing precision. Common values are 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, or 64. - Enter the Lead Screw or Belt Pitch
Lead screws have a pitch (distance traveled per full revolution of the screw). Belts have a tooth pitch. Enter the value in millimeters. - Enter Gear Reduction Ratio
If you are using gears or pulleys, enter the gear reduction ratio. Use 1 if your motor is directly driving the lead screw. - Click “Calculate”
The calculator instantly displays the distance traveled per motor step in millimeters.
Understanding the Result
The calculator shows the step distance:
- This is the linear distance moved by the CNC axis for each individual step of the stepper motor.
- Smaller step distances increase accuracy and smoothness of motion but may require higher microstepping or slower speeds.
- Larger step distances are faster but may sacrifice precision.
You can adjust micro stepping, lead screw pitch, or gear ratio to fine-tune the machine’s performance. For instance, reducing step distance improves engraving quality, while increasing it speeds up material removal during rough cuts.
Step Distance Formula
For reference, the formula used is:
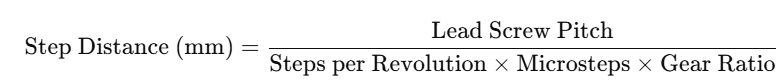
This formula accounts for all essential variables that affect CNC axis movement. Our calculator performs this calculation automatically, saving time and eliminating potential human errors.
Tips for CNC Accuracy
- Verify Motor Specifications – Always check your motor datasheet for the exact steps per revolution.
- Choose Appropriate Microstepping – High microstepping values increase smoothness but may reduce torque.
- Check Mechanical Tolerances – Lead screws, belts, and pulleys may have small manufacturing variations.
- Calibrate and Test – After calculating step distance, always test with a small move command to verify actual movement.
- Document Your Settings – Record your motor steps/mm and microstepping configuration for future reference.
Common FAQs
Q: Can I use this calculator for 3D printers?
Yes. Most 3D printers use stepper motors and lead screws or belts. Enter the printer’s stepper parameters for accurate results.
Q: What is microstepping, and why does it matter?
Microstepping divides each full motor step into smaller increments, increasing precision and smoothness of motion. Higher microstepping reduces step distance.
Q: Can gear ratios change the step distance?
Absolutely. If your motor drives the lead screw through gears or pulleys, the effective step distance changes proportionally to the gear ratio.
Q: Why is my calculated step distance different from actual movement?
Mechanical imperfections, loose belts, or incorrect specifications can cause discrepancies. Always verify with test movements.
Conclusion
Accurate CNC movement starts with understanding step distance. Our CNC Step Distance Calculator provides a simple, reliable way to calculate the exact distance each step of your motor moves. By combining motor steps, microstepping, lead screw pitch, and gear ratio, you can optimize your CNC machine for precision, speed, and reliability.
Whether you are a hobbyist, engineer, or professional CNC operator, this tool ensures you always have the accurate data needed for smooth, precise machini
